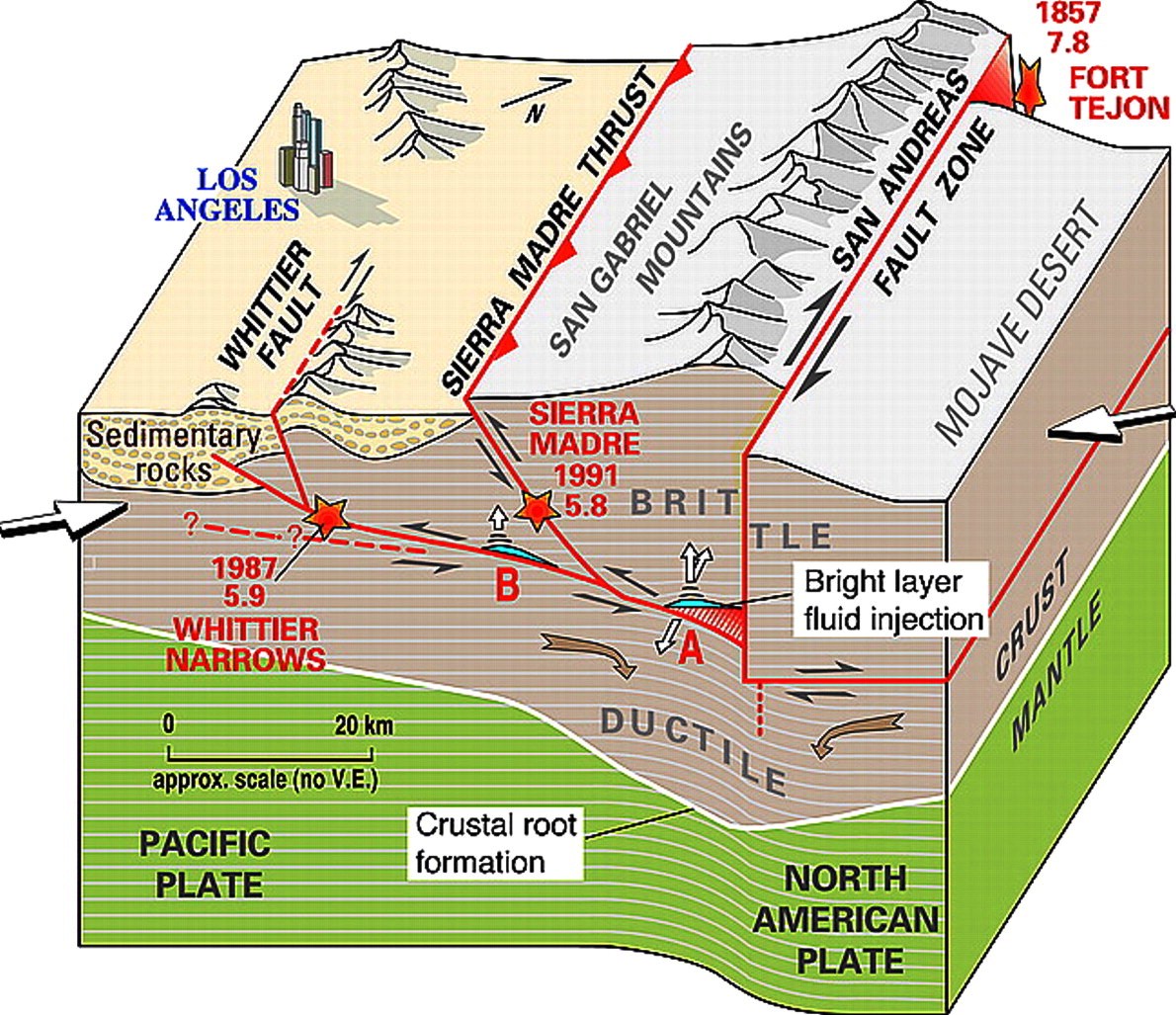
California is no stranger to earthquakes, with the infamous San Andreas Fault being the epicenter of seismic activity in the region. These natural disasters have shaped the landscape and lives of Californians for centuries. Understanding the intricacies of California earthquakes, especially in relation to the San Andreas Fault, is crucial for residents and those interested in the geological phenomena that define this vibrant state. This article delves into the history, mechanics, risks, and preparations related to earthquakes in California, providing insights to ensure safety and awareness.
From the devastating impacts of major earthquakes to the science behind tectonic plate movements, it's essential to grasp the underlying factors that contribute to seismic events. The San Andreas Fault, a transform fault that runs approximately 800 miles through California, plays a significant role in the state's earthquake landscape. The fault is a product of the Pacific and North American tectonic plates sliding past each other, creating tension and potential for significant geological shifts.
This comprehensive guide will cover various aspects of California earthquakes, including their history, frequency, and safety measures. With expert insights and reliable data, readers will gain a deeper understanding of how to prepare for and respond to seismic risks. Whether you are a California resident or merely interested in geology, this article aims to provide valuable information that emphasizes the importance of earthquake preparedness.
Table of Contents
- 1. History of Earthquakes in California
- 2. The San Andreas Fault: An Overview
- 3. Mechanics of Earthquakes
- 4. Assessing Earthquake Risks
- 5. Earthquake Preparedness
- 6. Emergency Response Plans
- 7. Future Predictions and Research
- 8. Conclusion
1. History of Earthquakes in California
California has a rich and tumultuous history marked by significant earthquakes. Major seismic events include:
- The 1906 San Francisco Earthquake: One of the most devastating earthquakes in American history, it had a magnitude of 7.9 and caused widespread destruction.
- The 1989 Loma Prieta Earthquake: Occurring during the World Series, this 6.9 magnitude quake resulted in 63 fatalities and extensive damage.
- The 2014 South Napa Earthquake: A magnitude 6.0 quake that caused significant property damage but no fatalities.
These events exemplify the dangers posed by the San Andreas Fault and similar geological features in California. Understanding this history is vital for recognizing the ongoing risks faced by residents.
2. The San Andreas Fault: An Overview
The San Andreas Fault is a major geological feature that is pivotal in California's seismic activity. Here are some key points:
- Location: The fault runs from the Salton Sea in Southern California to Cape Mendocino in the north.
- Type: It is classified as a transform fault, where two tectonic plates slide past each other horizontally.
- Segmentation: The fault is divided into several segments, each with different levels of seismic risk and historical activity.
2.1 Data and Statistics on the San Andreas Fault
Here are some statistics regarding the San Andreas Fault:
- The fault has a slip rate of approximately 20 mm per year.
- It has produced several major earthquakes in the past, with an average interval of about 150 years between significant seismic events.
- Recent studies suggest that the next major earthquake could occur within the next few decades.
3. Mechanics of Earthquakes
Understanding the mechanics of earthquakes is essential for recognizing how they occur:
- Tectonic Plates: The Earth's crust is divided into several tectonic plates that constantly move.
- Stress Accumulation: As these plates move, stress builds up at the fault lines until it is released as an earthquake.
- Magnitude and Intensity: The magnitude of an earthquake measures the energy released, while intensity measures its effects on people and structures.
3.1 The Role of the San Andreas Fault in Earthquake Generation
The San Andreas Fault is directly responsible for many of California's significant earthquakes. Its movement creates stress that can lead to:
- Shallow earthquakes, which tend to be more damaging.
- Long periods of relative quiet, followed by sudden, intense seismic activity.
4. Assessing Earthquake Risks
Risk assessment is crucial for understanding how likely it is for an earthquake to occur and its potential impact:
- Seismic Hazard Maps: California uses seismic hazard maps to identify and communicate earthquake risks across the state.
- Building Codes: The state has strict building codes designed to minimize earthquake damage.
- Insurance: Earthquake insurance is recommended for homeowners in high-risk areas.
5. Earthquake Preparedness
Preparedness is key to minimizing the impact of earthquakes:
- Emergency Kits: Having an emergency kit with supplies such as food, water, and first-aid materials is essential.
- Communication Plans: Families should establish communication plans to stay connected during an emergency.
- Drop, Cover, and Hold On: This is the recommended action during an earthquake to protect oneself from falling debris.
6. Emergency Response Plans
California has established emergency response plans to address the aftermath of earthquakes:
- State and Local Agencies: Agencies like Cal OES coordinate disaster response efforts.
- Community Training: Many communities offer training sessions for residents on how to respond to earthquakes.
- Public Alerts: The state utilizes public alert systems to warn residents of impending earthquakes.
7. Future Predictions and Research
Ongoing research is essential for predicting future seismic activity:
- Advancements in Technology: Scientists use advanced technology to monitor seismic activity and predict potential earthquakes.
- Research Initiatives: Various research initiatives focus on understanding earthquake patterns and improving safety measures.
- Public Awareness: Raising awareness about earthquake risks and preparedness is crucial for community resilience.
8. Conclusion
In summary, California's earthquake landscape is largely influenced by the San Andreas Fault, with a rich history of seismic activity shaping the region. Understanding the mechanics, risks, and preparedness measures associated with earthquakes is vital for residents. By staying informed and prepared, Californians can reduce the impacts of future earthquakes and ensure their safety.
We encourage readers to share their thoughts in the comments below, explore additional articles on earthquake preparedness, and stay informed about the latest developments in seismic research.
Thank you for taking the time to learn about California earthquakes and the San Andreas Fault. Stay safe and informed!